Introduction:
Assembler is a software program that converts the
assembly language to machine language. Machine languages consist entirely of numbers and are
almost impossible for humans to read and write. Assembly languages have the
same structure and set of commands as machine languages, but they enable a programmer
to use names instead of numbers. Each type of CPU has its own machine language
and assembly language, so an assembly language program written for one type of
CPU won't run on another. Programmers use assembly language when speed is
essential or when they need to perform an operation that isn't possible in a
high-level language. Assembler is the step comes in between a source code and
.exe file. The assembler creates object codes.
A two-pass assembler reads through the source code
twice. Each read-through is called a pass. On pass one the assembler doesn't write any code. It
builds up a table of symbolic names against values or addresses. On pass two,
the assembler generates the output code, using the table to resolve symbolic
names, enabling it to enter the correct values. The advantage of a two-pass
assembler is that it allows forward referencing in the source code because when
the assembler is generating code it has already found all references.
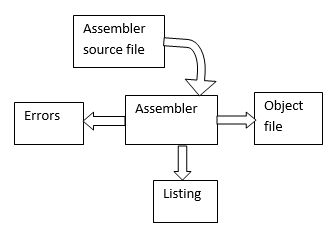 |
Fig: Different files
created by assembler
Project description:
This is the design of
assembler project as a mini project under the term paper topic of the system
software. In this project I will demonstrate how the assembler will produce and
interact with the various databases to convert the assembly language source
program to machine instruction that can be understood by the particular machine
after linking the object code using linker.
In this project I am going to develop the following
databases to convert source code in assembly language to object code
·
Symbol
table
·
Literal
table
·
Base
table
Technology to be used:
To convert the source code in
assembly language into the machine code c language is used.
Limitation:
As a
initial programmer in the field of designing the assembler, in this project I
have taken one static example to show how assembler generate the various
databases and interact through those database in first pass and second pass to
convert the source code into the object code. Although assembler generate
object code(.obj), assembly listing(.lst) and cross reference file(.crf), here
Iam going to generate only the object code.
Further scope:
Although
as a initial programmer in the field of assembler design I have taken a static
example for this project, It can be develop on generalized assembler that will
work for every source code that user will give as a input.
C code
//Design of
assembler
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void
print(char *p,int loc,int len,char ra);
void main()
{
char
*p[9][4] = {{"PRG1","START","",""},
{"","USING","*","15"},
{"","L","1","FIVE"},
{"","A","1","FOUR"},
{"","ST","1","TEMP"},
{"FOUR","DC","F'4'",""},
{"FIVE","DC","F'5'",""},
{"TEMP","DS","1F",""},
{"","END","",""}};
int i,j=0,location_counter=0;
int regno;
clrscr();
printf("\n");
printf(" Source code in assembly language is as
follows:\n");
printf("------------------------------------------------------\n");
for (i=0;i< 9;i++)
{
for(j=0;j< 4;j++)
{
printf("%s\t",p[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
getch();
printf("\n\nPress enter to
get the symbol for above assembly code.\n");
getch();
printf("\n Symbol Table:\n
");
printf("\nSYMBOL\tVALUE\tLENGTH\tRelocatable/Absolute\n");
printf("---------------------------------------------\n");
/*code for symbol table*/
for(i=0;i< 9;i++)
{
if(strcmp(p[i][1],"START")==0)
{
print(p[i][0],location_counter,1,'R');
}
else if(strcmp(p[i][0],"")!=0)
{
print(p[i][0],location_counter,4,'R');
location_counter=4+location_counter;
}
else
if(strcmp(p[i][1],"USING")==0)
{
}
else
{
location_counter=4+location_counter;
}
}
printf("----------------------------------------\n");
getch();
clrscr();
//code for literal table
printf("\n\nPress enter to get
the literal table for above assembly code.\n");
getch();
printf("\n Literal Table:\n
");
printf("\nLiteral\tVALUE\tLENGTH\tRelocatable/Absolute\n");
printf("---------------------------------------------\n");
location_counter=0;
for(i=0;i<9;i++)
{
if((strcmp(p[i][2],"F'4'")==0)||(strcmp(p[i][2],"F'5'")==0))
{
print(p[i][2],location_counter,4,'R');
location_counter=4+location_counter;
}
else
if((strcmp(p[i][0],"")==0)&&(strcmp(p[i][1],"USING")!=0))
{
location_counter=4+location_counter;
}
}
printf("-----------------------------------------------");
getch();
/* code for
base table */
printf("\nPress enter to get the Base
table for above assembly code.\n");
getch();
printf("\n Base Table:\n
");
printf("\nReg.No\t
Avalibility Indicator\t Content of base Reg.\n");
printf("\t(1 byte
character) \t\n");
printf("------------------------------------------------------\n");
regno=0;
for(i=0;i<=15;i++)
{
if(regno!=15)
{
printf("%d\t\t'N'\t\t
-\n",regno);
regno++;
}
else
{
printf("%d\t\t'Y' \t\t\n
",regno);
}
}
printf("-------------------------------------------------------");
getch();
}
//-----------------------------------------
void
print(char *p,int loc,int len,char ra)
{
printf("%s\t%d\t%d\t%c\n",p,loc,len,ra);
}
##End##

No comments:
Post a Comment